It is a potentially dangerous medical procedure with long-lasting consequences. Make certain the reasons are not transient.
⚠️ Use Discretion: Graphic human anatomy.
A Surge in Silicone
October Breast Cancer Awareness Month
Augmentation mammoplasty—commonly called breast augmentation—continues to be one of the most popular cosmetic surgical procedures. Surgeons perform hundreds of thousands of mammoplasties every year in the United States. Those aged 19–34 make up 48 percent of the patients. Forty percent of the procedures carried out in 2018 were on patients 35–50 years of age.
Why People Get Breast Implants
There are emotional, medical, and cosmetic reasons for augmentation mammoplasty. A properly fitted brassiere can address many aesthetic concerns:
- Reconstruction following mastectomy.
- Look better with and without clothing.
- Recover breast appearance after pregnancy.
- Correct uneven breasts.
- Satisfy body dysmorphic disorder.
- Correct congenital micromastia.
- Increase positive self-image perception.
- Elevate sagging breasts (mastopexy).
- Cosmetic MTF gender reassignment.
- Retain female figure of women bodybuilders.
People with Poland syndrome are born with pectoral muscles absent or underdeveloped on one side of the body. Some women may choose to have an implant to balance out breast asymmetry or lack of cleavage.

Excised breast due to carcinoma.
Types of Augmentation
The typical 60–90 minute operation involves:
- Making an incision in the skin next to or below the breast.
- Positioning the implant—either between breast tissue and chest muscle, or behind the chest muscle.
- Stitching the incision and covering it with a dressing.
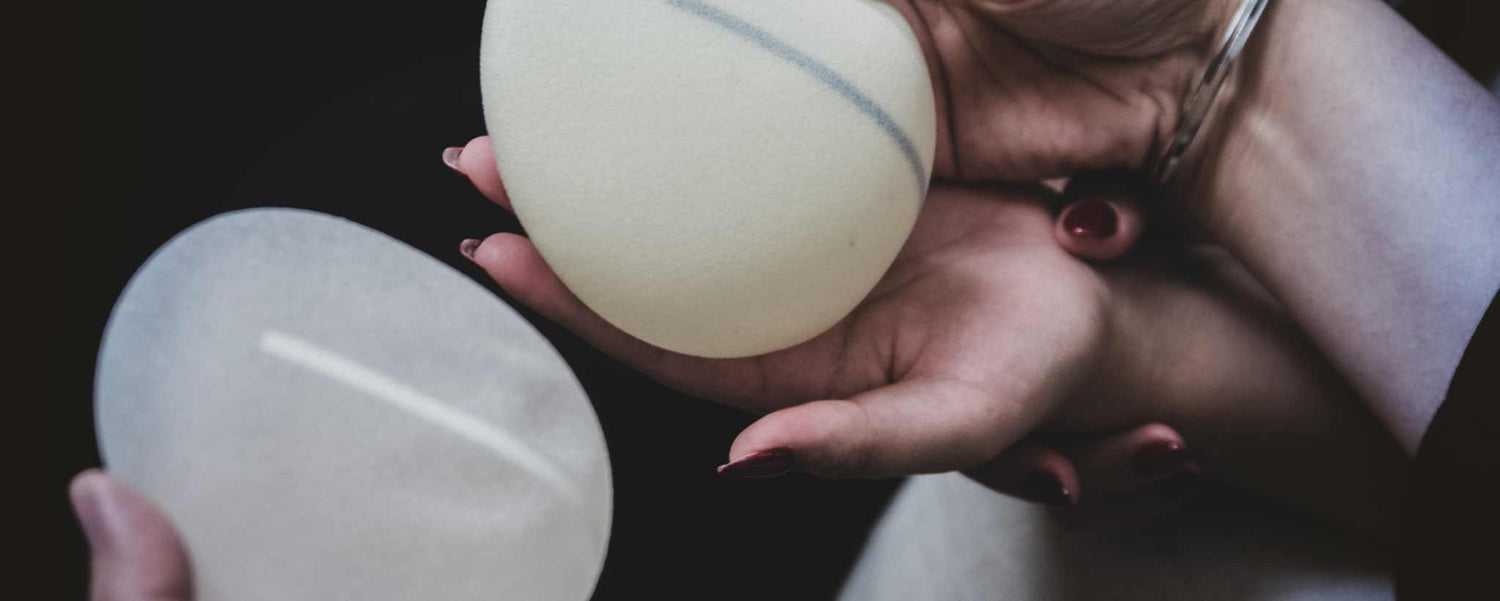
Form-stable implants are sometimes referred to as gummy bear breast implants because they maintain their shape even when the implant shell breaks. Saline-filled breast implants have a silicone outer shell filled with a sterile saltwater (saline) solution. When a saline breast implant ruptures, leaks, and empties, it quickly deflates. The sack is then surgically removed.
Silicone gel implants feel more like natural breasts than saline. When a silicone breast implant ruptures it usually does not deflate. The filler silicone leaks. Fourth- and fifth-generation implants are manufactured with double walls to minimize leaks.
Because of the eventual deflation of saline implants and the clinical effectiveness and safety of fourth- and fifth-generation silicone implants, silicone is now preferred over saline by most patients and physicians worldwide. Saline is sometimes recommended for younthful patients.
Employ only reputable plastic surgeons—with strong recommendations or make selection after interviewing several. Desired elevation, shape and firmness affect implant options—smooth or textured, round or teardrop shaped, saline, silicone, form-stable or fat-grafting.
Within a multistage reconstruction, a temporary implant expander, regulated by the FDA, is inserted to enlarge the implant pocket, thereby accommodating the breast implant prosthesis. Read product labeling accompanying each implant carefully.
In most instances of autologous fat-graft breast augmentation, a woman can expect an increase of one brassiere cup-size or less. Your own fat is relocated from excess elsewhere on your body. Therefore, you do not have to worry about implant failure or exchange.
Predictable, reliable, and consistent outcomes remains a significant challenge for fat-grafting due to the high variability in graft volume retention. You lose as much as 40–60 percent of the fat volume injected through necrosis or resorption. An increase of more than one cup size requires implants.
 During mastopexy (breast lift), the plastic surgeon raises sagging breasts by changing and modifying their size, contour, and elevation. The surgeon removes excess glandular and adipose tissues, overstretched suspensory ligaments, and excess skin from the skin-envelope. The nipple-areola complex is then repositioned higher upon the breast hemisphere.
During mastopexy (breast lift), the plastic surgeon raises sagging breasts by changing and modifying their size, contour, and elevation. The surgeon removes excess glandular and adipose tissues, overstretched suspensory ligaments, and excess skin from the skin-envelope. The nipple-areola complex is then repositioned higher upon the breast hemisphere.
Implant Complications
Throughout the 1950s and 1960s, plastic surgeons used synthetic fillers—including silicone injections. This caused granulomas and breast hardening, leading to mastectomies. Silicone injections are no longer performed. The first silicone implant developed by Thomas Cronin, Frank Gerow and the Dow Corning Corporation augmentation mammoplasty was in 1962. Twenty-six years later the FDA began investigating breast implant failures.
The NHS lists most common side effects following breast implant surgery as temporary pain, swelling, bruising and a tight feeling in the chest for a few weeks. More serious side effects associated with breast implants—including cancer risks—have been explored for decades.
Not only are there risks during surgery and recovery, augmentation mammoplasty involves implanting foreign matter within your body. Medical grade silicones are generally grouped into three categories: non-implantable, short term implantable, and long-term implantable.
Materials approved as Class V and VI can be considered medical grade. A very small number of patients may have allergic reactions to the outer silicone prosthesis—even if medical grade.
Immediate complications include wound infection, periprosthetic infection, hematoma, seroma, altered skin and nipple sensation, hypertrophic scarring, or complications related to anesthesia. Also consider late complications. When a prosthesis containing silicone ruptures, gelatinous foreign matter is excreted within the body. If a prosthesis containing saline ruptures, salt water is expelled. In either event, asymmetry, mold toxicity, allergic reactions and other consequences are possible.
Long-Term Consequences
- Breast implants are not guaranteed to last a lifetime.
- Wrinkling or asymmetry is possible.
- Breast implants without mastopexy do not correct sagging breasts.
- Breast implants may hamper breastfeeding.
- Mammograms might be more complicated.
- Routine MRI scans may be required.
- Most insurance does not cover breast implants.
- Breast revision surgery is always more difficult than primary breast augmentation due to scar tissue and skin stretching.
The FDA has identified an association between breast implants and the development of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Individuals who have breast implants may have an increased risk of developing ALCL in the fluid or scar tissue surrounding the implant.
FDA Proposes Boxed Warning on Breast Implants
⚠️ October 23, 2019 – Breast implants are not lifetime devices; the chances of developing complications increase the longer a patient has the implant and additional surgery may be required to address the complications; breast implants have been associated with the risk of developing breast implant–associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) and may be associated with systemic symptoms, such as fatigue or joint pain. —Medscape
Capsular contracture occurs when scar tissue forms around breast implants. During capsular contracture, the breast may harden, look and feel different, as well as cause discomfort. This requires capsulotomy or revision surgery. Do not ignore gross photos and stories of bad outcomes. Understand them as well at the successes for a balanced view.
Allergan Pulls Textured Breast Implants in US and Worldwide
⚠️ July 24, 2019 – The FDA announced that Allergan is globally recalling all BioCell textured breast implant products. Of the 573 unique cases of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), 481 (84%) have been attributed to Allergan implants. —Medscape
The list of implant patients with regrets is swelling. Some opt for too large of a cup size. Others have complications from surgery, like Stephanie. After implant, infection, explant, implant, and another explant she says, “The scars are fading into fine white lines. My breasts are small, well proportioned, and just right for my body.” Amber regrets not having her surgeon perform a total an en bloc or capsulectomy during explant.
![]()
Silicone bra inserts are far less expensive (< $50) with a significant reduction in complications compared to invasive procedures. Worn externally, they may not match skin tone or size of a remaining breast. They are essentially bra padding, which suffice for some women. —Amazon.com
Emotional Considerations
Few females are totally satisfied with their breast appearance—with or without implants. Some people have regrets following augmentation because of scaring or the need for maintenance surgeries. Women have an overall threefold higher risk of suicide after getting breast implants, according to data analysis of 3,527 Swedish women. It is likely that there is an underlying psychological predisposition relating to self-esteem.
Your individual emotional, psychological and physiological expectations affect satisfaction with breast enlargement or reduction. Vanity, a desire to attract or satisfy a mate, low self-confidence, or health problems like backaches are considerations that should be discussed with your doctor and possibly a mental health professional.
Adolescent Augmentation
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) estimates more than 333,000 cosmetic procedures were performed on patients 18 years of age or younger in the United States in 2005, compared to approximately 14,000 in 1996.
Breast implant surgery is one of the two most popular and controversial cosmetic procedures for adolescents. Breast reduction may be necessary for juvenile gigantomastia (massive breast enlargement) or breast hypertrophy.
Usually beginning during adolescence, body dysmorphic disorder (BDD)—an atypical quest to “normalize” one’s appearance—affects up to 2.4 percent of the population. BDD shares a commonality with obsessive-compulsive disorder, but involves more depression and social avoidance.
Adolescents with congenital micromastia may wish to have breast augmentation. A teenage patient’s motivation and expectation for breast augmentation surgery should be directly addressed by parents and physician. With a focus on remaining ClinicalReads Health, it is difficult to justify purely esthetic surgery during this developmental period.
There are no standard protocols but preoperative assessment of adolescents should include evaluation of physical maturity, stability of body image, and emotional maturity. Physical maturity includes both stature and breast maturity.
Doctors should evaluate possible eating disorders or negative self-esteem issues. Breast augmentation is a potentially dangerous medical procedure with long-lasting consequences. Make certain the reasons are not transient.
Enjoy more articles about women
ClinicalPosters offers human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other services that compliment articles about women. Slide extra posters into DeuPair Frames without removing from the wall.
Show your support by leaving an encouraging comment to keep the research going.
Support the writing of useful articles about women by exploring human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products online. You may sponsor specific articles.
ClinicalPosters provides human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products that compliment useful articles about women.
ClinicalPosters offers human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products online.
You can sponsor scholarly articles about women or donate to further research. Some content may be inappropriate for younger audiences. Visible content is optimized for device size.







 Romance & Health Intertwine. Fall in love with a captivating romance miniseries that explores the essence of well-being. Become a ClinicalNovellas member for heartwarming tales.
Romance & Health Intertwine. Fall in love with a captivating romance miniseries that explores the essence of well-being. Become a ClinicalNovellas member for heartwarming tales.