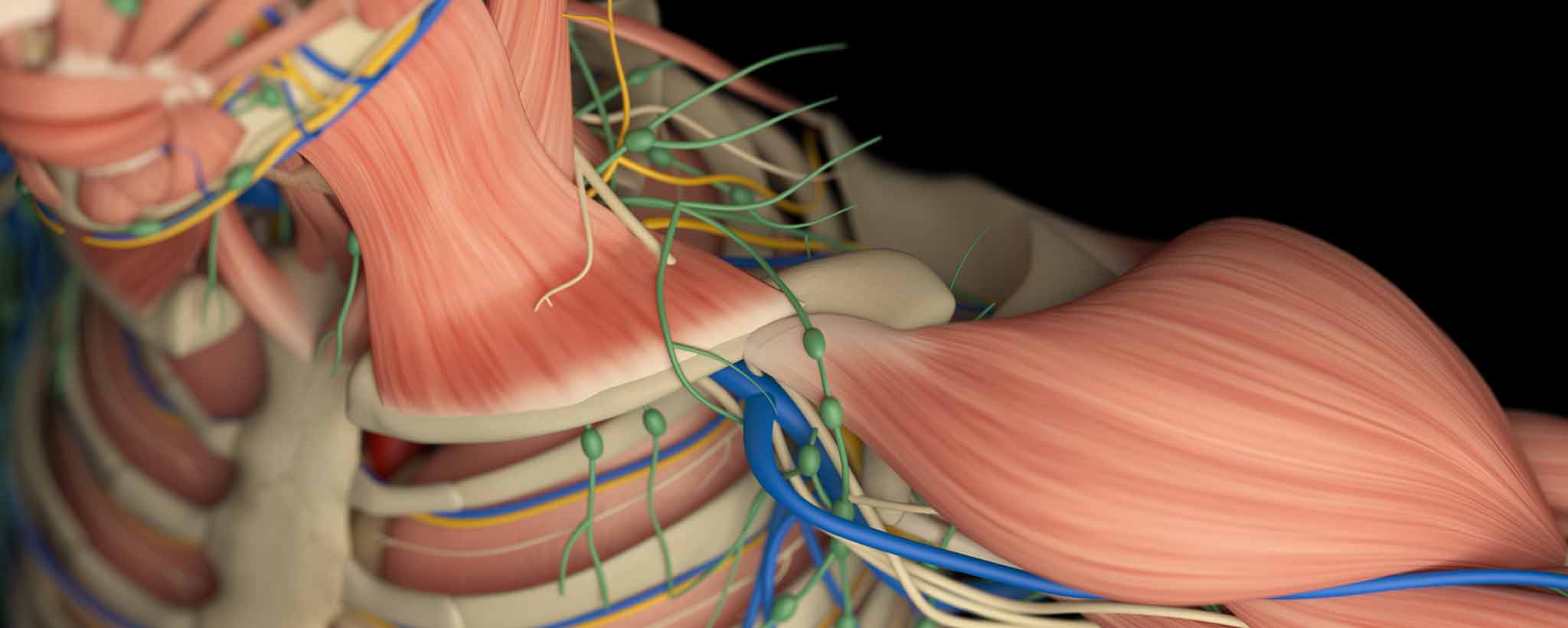
Regarded as more than a source of infant nutrition, women’s breasts are often viewed as symbols of femininity.
⚠️ Use Discretion: Graphic human anatomy.
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month
A cancer diagnosis can strike an emotional blow. Firstly, it forces women to face their own mortality. Secondly, a patient can’t help but wonder about post-operation disfigurement. So self-esteem is a valid concern to be addressed by oncologists and surgeons.
The first noticeable symptom of breast cancer is typically a lump that feels different from the rest of the breast tissue. More than 80 percent of breast cancer cases are discovered when a woman personally feels a lump.
The earliest breast cancers are generally detected by a mammogram. Lumps found in lymph nodes located within the armpits can also indicate breast cancer.
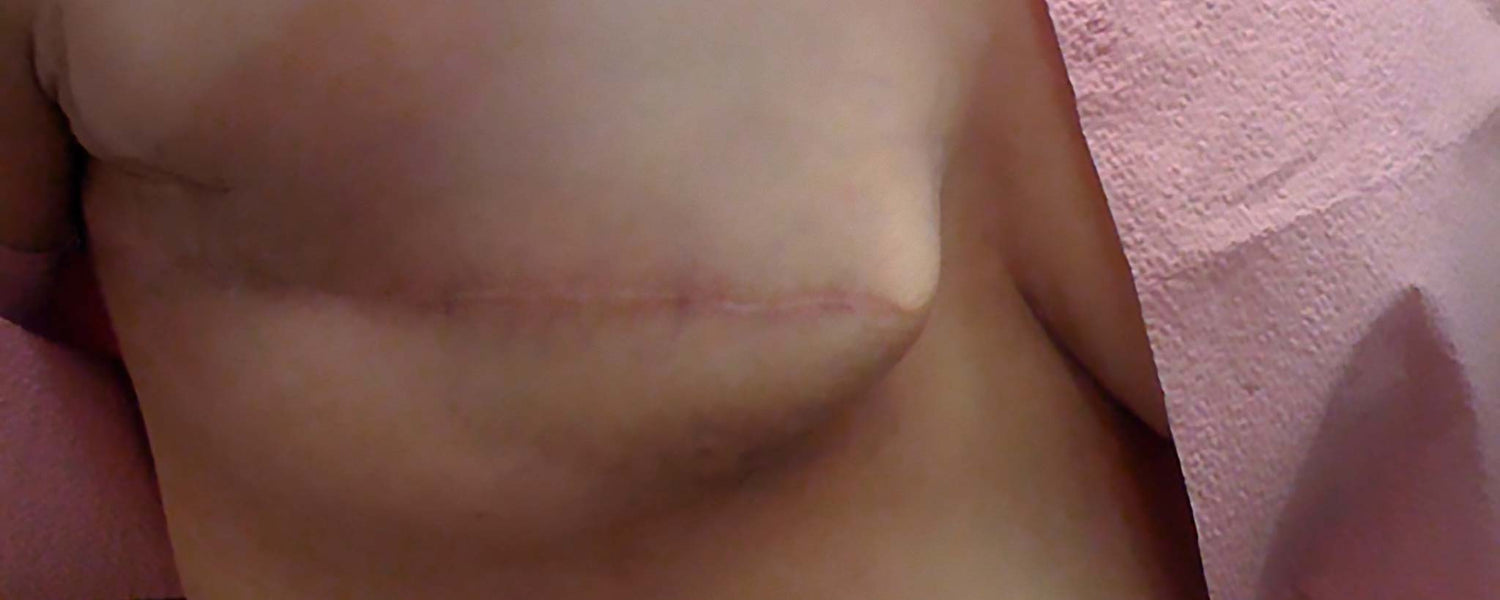
Lumpectomies preserve as much breast tissue as possible. During a radical mastectomy, the lymph nodes, breast tissue, the nipple and the dark area around it called the areola may be removed along with part of the underlying muscle. This leaves a prominent scar.
Surgeons prioritize curing cancer over aesthetics. However, radical mastectomy is not always required to halt the spread of the disease. Over the past decade, early detection and better techniques have diminished the frequency of radical mastectomies.
Is Breast Reconstruction Necessary?
Often dependent upon factors such as age, marital status, family support, and economics, women may decline breast reconstruction surgery. Insurance distinguishes between medical and cosmetic procedures, often requiring a significant financial expenditure for the latter. A cosmetic implant to restore volume can be performed by plastic surgeons.
Beyond the scope of typical dermatology doctors, areola simulation can be achieved via skin grafting and/or tattooing. Some patients may consider an areola as essential to reconstruction, while others who prefer to have no protrusion through clothing may forego any nipple reconstruction.
A woman unsatisfied with pre-surgical breast size or shape may have contemplated augmentation but decided against a solely cosmetic procedure. With a mastectomy under consideration, reconstruction surgery may provide an opportunity for a patient to achieve a more pleasing appearance than before the cancer surgery. If reconstruction is planned, skin-sparing (also called nipple-sparing or breast-sparing) mastectomy is something to be discussed with oncology and plastic surgeons.
Recognize that implanting foreign matter within your body carries risks. Some people have allergic reactions to silicone. Over time, implants decay.
Allergan Pulls Textured Breast Implants Worldwide
July 24, 2019 – The FDA announced that Allergan is globally recalling all BioCell textured breast implant products. Of the 573 unique cases of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), 481 (84%) have been attributed to Allergan implants. —Medscape
Can the Breast Be Spared?
Nipple-sparing mastectomy is the removal of affected breast tissue, without the removal of any of the skin, nipple, or the areola. Patients undergoing prophylactic mastectomies like Angelina Jolie with high risk but no cancer detection are ideal candidates for nipple-sparing or breast-conserving mastectomy.

Typically, one incision is made in the armpit and another below the breast, where it meets the chest to facilitate the removal of breast tissue. This can maintain an ideal repository for implantation or perhaps even eliminate the need for reconstruction.
Two weeks before her nipple-sparing mastectomy, Jolie had an uncommon nipple-delay procedure performed. This severs blood vessels and other breast tissue beneath the nipple so it can become accustomed to getting blood supply from the surrounding skin. This increases the chances of post-op nipple survival—particularly in patients who have had prior breast surgery.
More than 80% of breast cancer cases are discovered when the woman feels a lump.
Variations of breast-conserving surgery include lumpectomy (removal of the lump), quadrantectomy (removal of one quarter, or quadrant, of the breast), and segmental mastectomy (removal of the cancer as well as some of the breast tissue around the tumor and the lining over the chest muscles below the tumor).
Improvements in the total skin-sparing mastectomy technique have resulted in a successful intervention with high nipple viability and low rates of recurrence when cancer is detected early.
In multiple studies, skin-sparing mastectomy seems to be oncologically safe in patients undergoing mastectomy for invasive T1-T2 tumors, multicentric tumors, ductal carcinoma in situ or risk-reduction. But it is not a viable option for everyone. It should be avoided in patients with inflammatory breast cancer or those with extensive tumors affecting the skin or nipple.

Breast cancer tumor
Psychological Impact of Mastectomy
Some feel a sense of empowerment and freedom following a mastectomy. Matuschka became a public model who proudly displayed her surgical scars in the August 1993 issue of The New York Times Magazine. Amidst criticism from members of The SCAR Project, she underwent reconstructive surgery 20 years later.
One reader wrote The New York Times after seeing the cover: ‘Now everyone has to know what I look like—I’ve hidden it from my husband all these years, and now you had to expose it.’ This well illustrates how one’s perception of this admirable aspect of female anatomy can be altered when facing surgery, immediately following mastectomy, and years later.
Is Chemotherapy Necessary?
A study of 10,273 women, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, analyzed how well a widely used genetic test assesses cancer risk, based on 21 genes linked with breast cancer recurrence.
“With these genomic tests, we are finding that we have multiple types of breast cancer, perhaps several dozen,” said Dr. Otis Brawley, chief medical and scientific officer for the American Cancer Society, who was not part of the study, “and we are being able to tailor our therapies to the type of breast cancer every woman has.”
A 15-minute procedure called laparoscopic cryoablation is in global clinical trials and practice. A needle connected to a machine guides the tip to the tumor and then freezes and removes it like an ice cube, without damaging surrounding tissue. Ask your doctor if you are a viable candidate.
Enjoy more articles about women.
ClinicalPosters offers human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other services that compliment articles about women. Slide extra posters into DeuPair Frames without removing from the wall.
Show your support by leaving an encouraging comment to keep the research going.
Support the writing of useful articles about women by exploring human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products online. You may sponsor specific articles.
ClinicalPosters provides human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products that compliment useful articles about women.
ClinicalPosters offers human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products online.
You can sponsor scholarly articles about women or donate to further research. Some content may be inappropriate for younger audiences. Visible content is optimized for device size.





 Romance & Health Intertwine. Fall in love with a captivating romance miniseries that explores the essence of well-being. Become a ClinicalNovellas member for heartwarming tales.
Romance & Health Intertwine. Fall in love with a captivating romance miniseries that explores the essence of well-being. Become a ClinicalNovellas member for heartwarming tales.