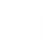
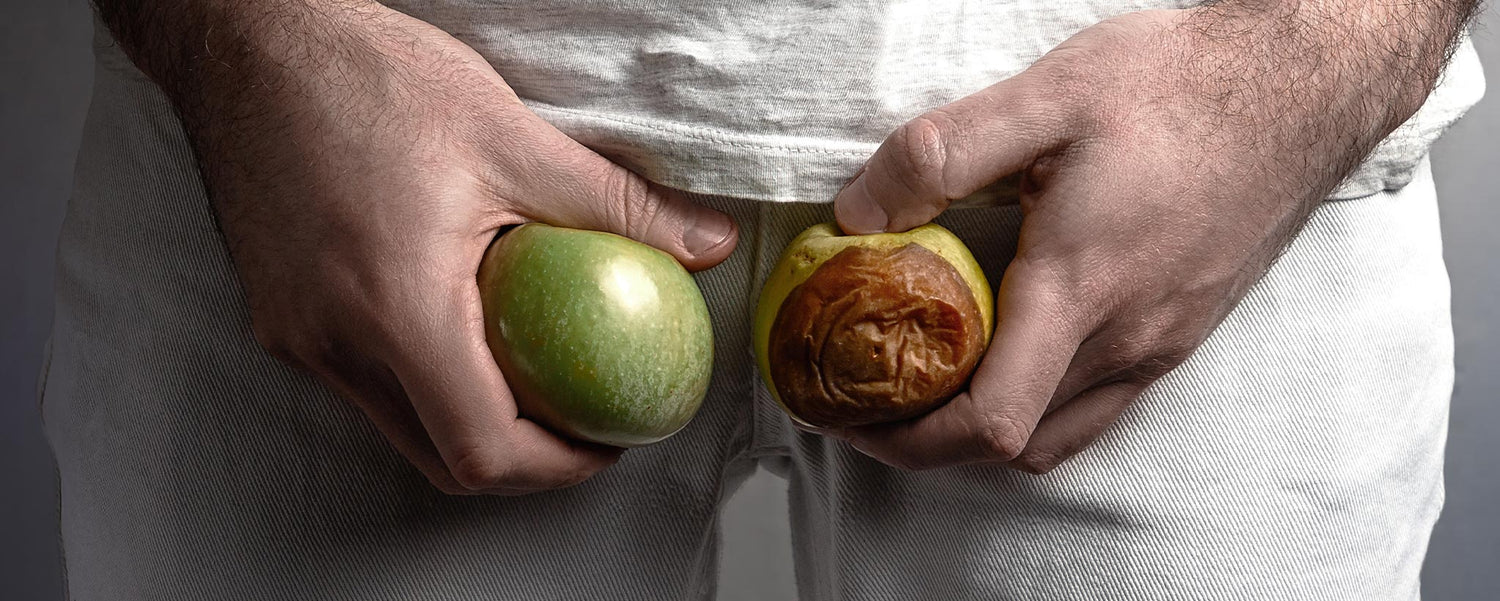
Paradoxically, this infrequent carcinoma within the male genitals is the number-one cancer in men ages 20 to 34, which can also spread outside the testicles.
⚠️ Use Discretion: Graphic human anatomy.
Rare But Dangerous
Of all cancers, at 1 percent, testicular cancer is very rare. There are fewer than 20,000 cases per year reported in the United States. Paradoxically, this infrequent carcinoma within the male genitals that manufactures hormones and sperm is the number one cancer in men ages 20–34. With early detection, survival rate is over 90 percent.
Testicular Cancer Symptoms
Having a high survival rate, the most important question to you, perhaps, is how do you rule it out—or how is it detected early? The most common symptom is a lump on a testicle (which differs from the dermal bump). Swelling of the testicle (with or without pain) or a feeling of weight within the scrotum may be detected.
Carcinoma can also spread outside of the testicles. This can cause unusual abdominal discomfort. Utilizing the lymphatic system, pain can also be felt in your lower back. Coughing can produce shortness of breath. If it travels to the lymph nodes in your chest, your nipples may feel tender.
It is fairly easy to check for lumps while cleaning up in the shower or bath. Regular examination allows you to detect subtle differences. Do not confuse a testicular lump with the epididymis—a convoluted duct behind either testicle.
Schedule an appointment with a urologist soon after a lump is discovered. A blood test is warranted. Ultrasound can help determine if the lump is solid or filled with fluid.
As the name implies, testicular carcinoma originates as a lump within a testicle.
Treatment For Testicular Cancer
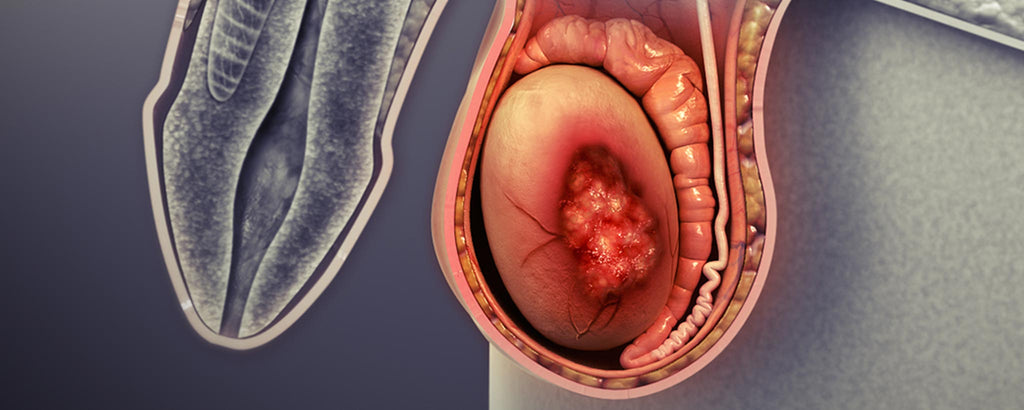
Treatment options depend upon the stage at which the tumor is discovered. Radiation, chemotherapy, or radical orchiectomy (also called orchidectomy or testectomy). The latter removes the spermatic cord along with the testicle and tumor.
Testicular mass causes other than a testicular tumor need to be excluded before radical orchiectomy is performed. If you have orchiectomy due to cancer, your doctor may follow up with chemotherapy or radiation to lower the chances that any leftover cancer cells spread.
Orchiectomy is a surgical procedure in which one or both testicles are removed (bilateral orchiectomy). This is sometimes performed for advanced testicular cancer, prostate cancer or testicular torsion.
After treatment with radical orchiectomy and external-beam radiation therapy, the 5-year disease-free survival rate is 98 percent for stage I tumors and 92–94 percent for stage IIA tumors. For a higher-stage disease that has been treated with radical orchiectomy followed by chemotherapy, the 5-year disease-free survival rate is 35–75 percent.
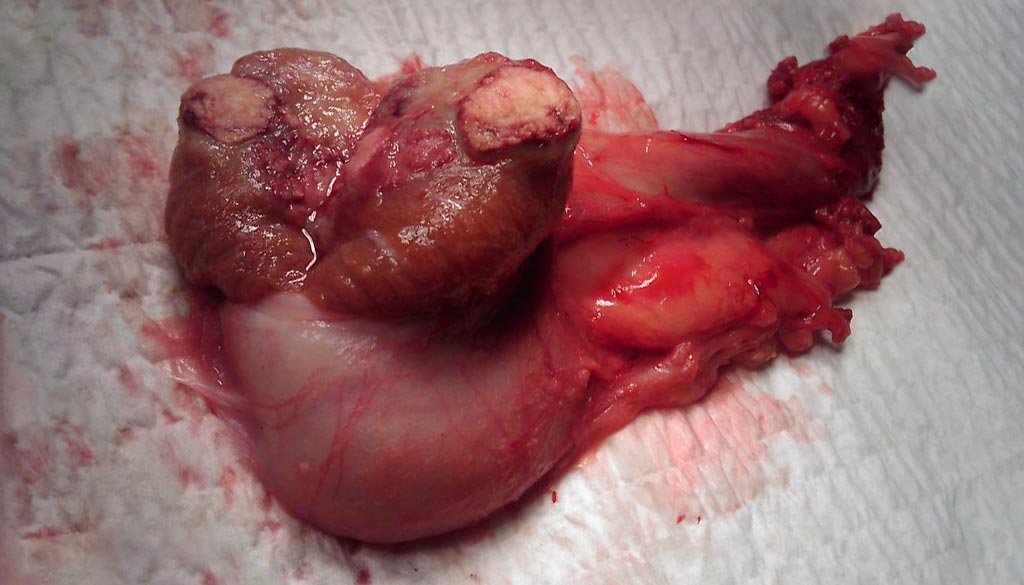
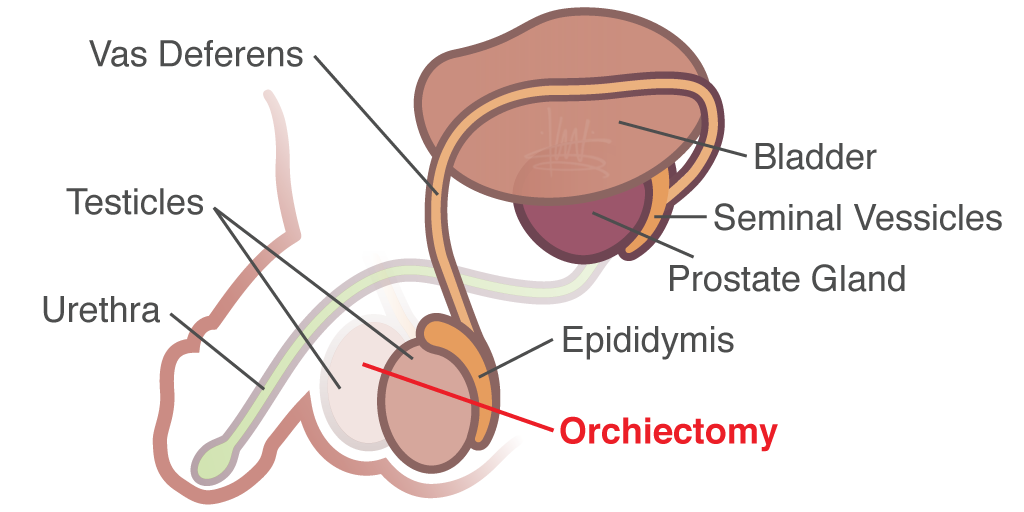
Orchiectomy testicle photographed with patient’s permission. —Alfred Bester
Certain treatments cause temporary or permanent infertility. If you are diagnosed with testicular cancer, but still want to have children, sperm banking before undergoing any treatment is recommended.
Enjoy more articles about oncology.
ClinicalPosters offers human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other services that compliment articles about oncology. Slide extra posters into DeuPair Frames without removing from the wall.
Show your support by leaving an encouraging comment to keep the research going.
Support the writing of useful articles about oncology by exploring human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products online. You may sponsor specific articles.
ClinicalPosters provides human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products that compliment useful articles about oncology.
ClinicalPosters offers human anatomy charts, scientific posters, and other products online.
You can sponsor scholarly articles about oncology or donate to further research. Some content may be inappropriate for younger audiences. Visible content is optimized for device size.
UPDATED 2026 – This article reflects editorial revisions since its original publication.
FAQ: Testicular cancer concerns
How common is testicular cancer?
There are fewer than 20,000 cases per year reported in the United States. With early detection, the survival rate is over 90 percent.
What are the symptoms of testicular cancer?
The most common symptom is a lump on a testicle (which differs from the dermal bump). Swelling of the testicle (with or without pain) or a feeling of weight within the scrotum.
What is the treatment for testicular cancer?
Treatment options depend upon the stage at which the tumor is discovered. Radiation, chemotherapy, or radical orchiectomy—a surgical removal of one or both testicles.
Is a man able to father children after treatment?
Temporary or permanent infertility is possible. When diagnosed with testicular cancer, consider sperm banking before undergoing any treatment.






 Romance & Health Intertwine. Fall in love with a captivating romance miniseries that explores the essence of well-being. Become a ClinicalNovellas member for heartwarming tales.
Romance & Health Intertwine. Fall in love with a captivating romance miniseries that explores the essence of well-being. Become a ClinicalNovellas member for heartwarming tales.